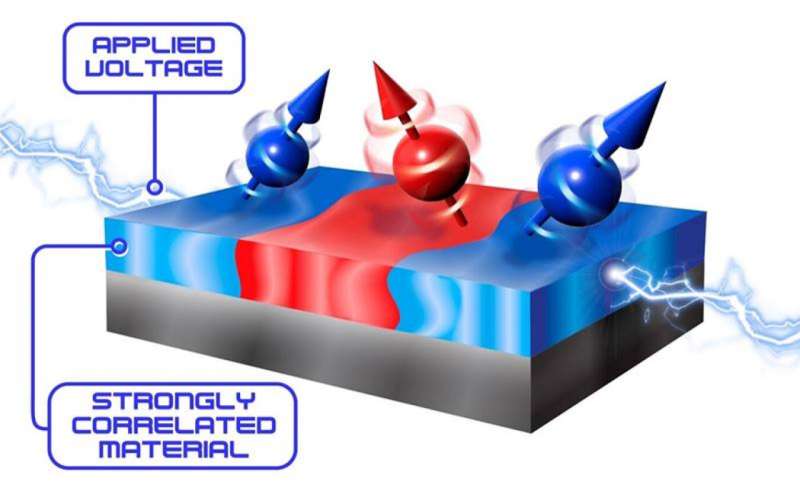
A team of researchers has discovered a new way to control the magnetic behavior of quantum materials using applied voltages. Specifically, the material lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO), which is magnetic and metallic at low temperatures but non-magnetic and insulating when relatively warm, can be influenced by voltage.
The work is published in the journal Nano Letters.
Quantum materials like LSMO are materials that possess special properties because of the rules of quantum mechanics. Researchers discovered that applying voltage to LSMO in its magnetic phase causes the material to split into regions with distinct magnetic properties. The magnetic properties of these regions depend on the applied voltage. This is important because normally, magnetic properties don’t respond to voltage.
However, in LSMO, voltage can be used to tune different magnetic regions in the same material. This breakthrough could lead to energy-efficient methods for controlling magnetism.
Tuning a material’s magnetism with an applied voltage is one way to develop circuits that mimic how the human brain processes information, also known as neuromorphic circuits. Another approach is tuning a material’s resistance to switch from a low to a high value and vice versa. In LSMO, both resistance and magnetism can be tuned. This creates a new path to the realization of neuromorphic devices.
The researchers detected this phenomenon using a ferromagnetic resonance technique, which allows scientists to observe changes in the magnetic characteristics of LSMO under different voltage levels. In the ferromagnetic resonance technique, a peak is observed when the precession of the material’s magnetization matches the frequency of an incoming electromagnetic wave.
The experiments on LSMO measured multiple peaks, indicating that the material contained multiple magnetic phases. In each of these phases, the electron spins oscillated at a different frequency, producing different peaks. In addition, small changes in the applied voltage induced large changes in the oscillation frequencies.
The researchers discovered that LSMO is a material that can be used both for switching between high and low electrical resistance states and for spintronic applications, offering new possibilities for spintronic neuromorphic devices.
This result is important because it provides a path to improve the performance of neuromorphic circuits based on spin oscillator networks, also known as spintronic neuromorphic devices. These devices hold great potential for improving artificial intelligence, leading to smarter, faster, and more energy-efficient information processing technologies.
More information:
Tian-Yue Chen et al, Electrical Control of Magnetic Resonance in Phase Change Materials, Nano Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c02697
Provided by
US Department of Energy
Citation:
Tuning magnetism with voltage opens a new path to spintronic neuromorphic circuits (2025, January 16)
retrieved 16 January 2025
from https://phys.org/news/2025-01-tuning-magnetism-voltage-path-spintronic.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.