Plasmons are collective oscillations of electrons in a solid and are important for a wide range of applications, such as sensing, catalysis, and light harvesting. Plasmonic waves that travel along the surface of a metal, called surface plasmon polaritons, have been studied for their ability to enhance electromagnetic fields.
One of the most powerful tools for studying these waves is time-resolved electron microscopy, which uses ultrashort laser pulses to observe how these plasmonic waves behave. An international research team recently pushed the boundaries of this technique.
As reported in Advanced Photonics, the researchers used multiple time-delayed laser pulses of four different polarizations to capture the full electric field of these waves. This method allowed them to achieve a level of accuracy previously not possible.
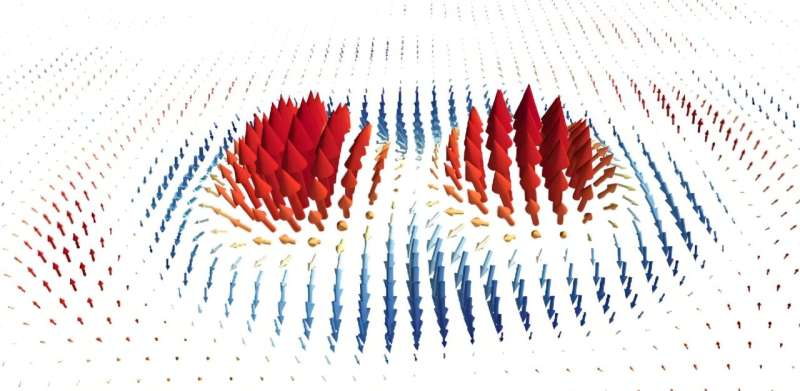
To test their technique, the team investigated a specific spin texture known as a meron pair. A meron is a topological structure where the direction of the spin texture only covers half of a sphere, which distinguishes it from other similar structures, like skyrmions, whose spin covers the entire sphere.
To reconstruct the spin texture from the experiment, the researchers needed the electric and magnetic field vectors of the surface plasmon polaritons. While the electric field vectors could be directly measured, the magnetic field vectors had to be calculated based on the electric field’s behavior over time and space.
By using their precise method, the researchers were able to reconstruct the spin texture and determine its topological properties, such as the Chern number, which describes the number of times the spin texture maps onto a sphere. In this case, the Chern number was found to be one, indicating the presence of a meron pair.
The study also demonstrated that the spin texture remains stable throughout the duration of the plasmonic pulse, despite the fast rotation of the electric and magnetic field vectors. This new approach is not limited to meron pairs and can be applied to other complex surface plasmon polariton fields.
Understanding these fields and their topological properties is important, especially at the nanoscale, where topological protection can help maintain the stability of materials and devices.
This research shows that it is now possible to study complex spin textures with high precision on extremely short timescales. The ability to accurately reconstruct the full electric and magnetic fields of surface plasmon polaritons opens new possibilities for exploring the topological properties of electromagnetic near fields, which may have important implications for future technologies at the nanoscale.
More information:
Pascal Dreher et al, Spatiotemporal topology of plasmonic spin meron pairs revealed by polarimetric photo-emission microscopy, Advanced Photonics (2024). DOI: 10.1117/1.AP.6.6.066007
Citation:
New electron microscopy technique reveals complex spin structures at femtosecond timescales (2024, December 20)
retrieved 22 December 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-12-electron-microscopy-technique-reveals-complex.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.