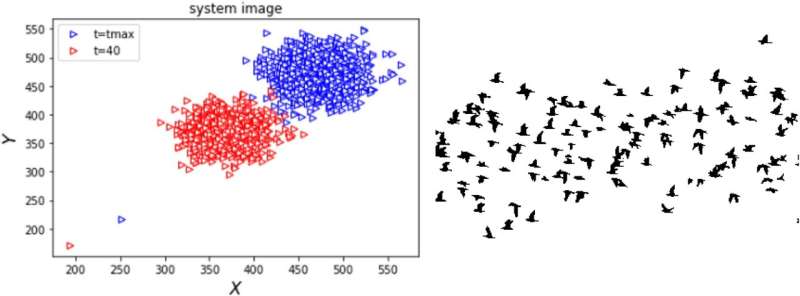
Phase transitions in the collective motions of self-propelled particles are directly impacted both by the initial velocity of each particle, and the repulsive radius surrounding them.
Collective motions of self-propelled particles can be found across many systems in nature. One of the most striking features of this phenomenon is the way in which systems transition between different states of motion: a behavior which can be compared directly with phase transitions in physics. So far, however, it is still not fully understood how these transitions are impacted by the initial parameters of these deeply complex systems.
Through analysis published in The European Physical Journal E, Salma Moushi and colleagues at the University of Hassam II, Morocco, show how the conditions required for transitions to occur are heavily dependent on the initial velocities of each particle, and the repulsion radius surrounding them.
The team’s insights could lead to a deeper understanding of motion in a diverse array of natural systems, including the behavior of bacteria, the dynamics of large groups of fish, birds, and insects, and even the movements of people within large crowds.
For a system of self-propelled particles to transition into an ordered phase, it first needs to satisfy two key conditions: it must have a sufficiently high density, and be below a certain critical noise. Once these conditions are met, coherent, large-scale structures can emerge, where many particles move in the same direction.
However, Moushi’s team predict that both of these properties are heavily dependent on two further factors: the initial velocity of each particle, and the radius surrounding them where particles will repel their neighbors to avoid collisions.
To investigate the impact of these factors, the researchers studied simulated phase transitions using the ‘classical Vicsek model,’ which is often used to study the collective behaviors of self-propelled particles.
As they predicted, Moushi’s team concluded that density and critical noise were both directly dependent on the particles’ initial velocity and repulsion radius.
Due to their dependence on both of these factors, this ultimately means that the nature of phase transitions can vary widely, depending on the starting conditions of individual particles.
More information:
I. Tarras et al, Effect of repulsive interaction and initial velocity on collective motion process, The European Physical Journal E (2024). DOI: 10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00455-2
Citation:
Exploring the impacts of particle parameters on self-propelled motions (2025, January 6)
retrieved 6 January 2025
from https://phys.org/news/2025-01-exploring-impacts-particle-parameters-propelled.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.